refresh()3.1 prepareRefresh方法3.2 obtainFreshBeanFactory3.3 prepareBeanFactory3.4 postProcessBeanFactory3.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors3.6 registerBeanPostProcessors3.7 initMessageSource3.8 initApplicationEventMulticaster3.9 onRefresh3.10 registerListeners3.11 finishBeanFactoryInitialization3.12 finishRefresh
refresh()
该方法是 Spring Bean 加载的核心,它是 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的父类 AbstractApplicationContext 的一个方法 , 顾名思义,用于刷新整个Spring 上下文信息,定义了整个 Spring 上下文加载的流程。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//准备刷新上下文 环境
this.prepareRefresh();
//初始化BeanFactory,并进行XML文件读取
/*
* ClassPathXMLApplicationContext包含着BeanFactory所提供的一切特征,在这一步骤中将会复用
* BeanFactory中的配置文件读取解析及其他功能,这一步之后,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
* 实际上就已经包含了BeanFactory所提供的功能,也就是可以进行Bean的提取等基础操作了。
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//对beanFactory进行各种功能填充
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//子类覆盖方法做额外处理
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//激活各种beanFactory处理器
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理器,这里只是注册,真正的调用实在getBean时候
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//为上下文初始化Message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
this.initMessageSource();
//初始化应用消息广播器,并放入“applicationEventMulticaster”bean中
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//留给子类来初始化其它的Bean
this.onRefresh();
//在所有注册的bean中查找Listener bean,注册到消息广播器中
this.registerListeners();
//初始化剩下的单实例(非惰性的)
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
每个子方法的功能之后一点一点再分析,首先 refresh()方法有几点是值得我们学习的:
方法是加锁的,这么做的原因是避免多线程同时刷新 Spring 上下文;
尽管加锁可以看到是针对整个方法体的,但是没有在方法前加 synchronized 关键字,而使用了对象锁 startUpShutdownMonitor,这样做有两个好处:
(1)refresh()方法和 close()方法都使用了 startUpShutdownMonitor 对象锁加锁,这就保证了在调用 refresh()方法的时候无法调用 close()方法,反之依然,这样就避免了冲突。
(2)使用对象锁可以减小同步的范围,只对不能并发的代码块进行加锁,提高了整体代码运行的速率。
在 refresh()方法中整合了很多个子方法,使得整个方法流程清晰易懂。这样一来,方便代码的可读性和可维护性。
3.1 prepareRefresh方法
//设置启动时间,是否激活标识位,初始化属性源(property source)配置
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
this.logger.debug("Refreshing " + this.getDisplayName());
}
}
// 在上下文环境中初始化任何占位符属性源。(空的方法,留给子类覆盖)
this.initPropertySources();
//验证所有的必需的属性是否可解析,若无则不能解析并抛出异常
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet(this.applicationListeners);
} else {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();
}
prepareRefresh 的内容如上,该方法主要进行环境的准备,包括 Context 的启动时间,活动状态,然后设置 context 中的配置数据源,使用默认的 StandardEnvironment 对象,该对象添加了 System.env()属性和 System.properties()属性 。 initPropertySources 方法用于初始化 context 中 environment 的属性源。在 AbstractApplicationContext 中为空实现。其他子类的实现如下:
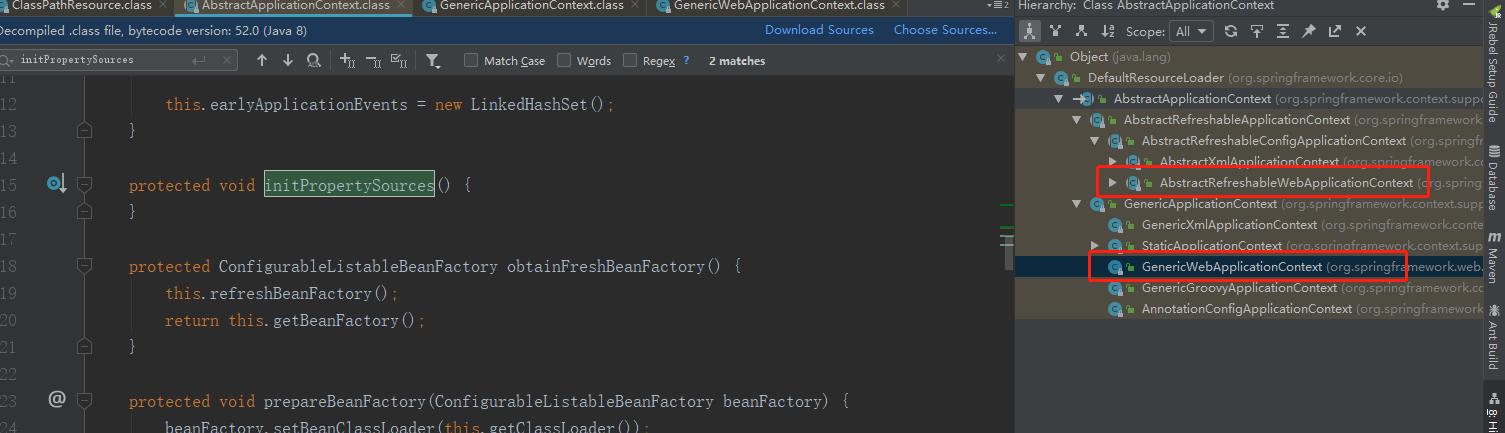
在子类 GenericWebApplicationContext 和 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 的实现大致一致,都是:
protected void initPropertySources() {
ConfigurableEnvironment env = this.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
}
通过在 getEnvironment 方法中,重写 createEnvironment 方法 。
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
将 AbstractApplicationContext 类中默认的 StandardEnvironment 替换为StandardServletEnvironment, StandardServletEnvironment 的关系图为:
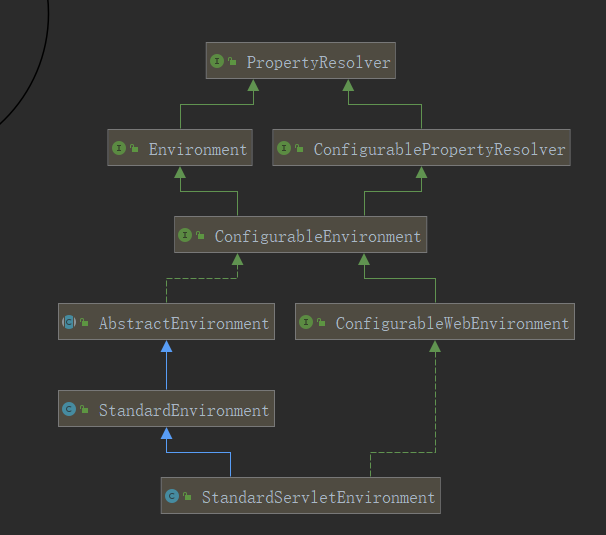
因而会执行 StandardServletEnvironment 类的 initPropertySources 方法,为 context 添加 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig 对应的配置属性源。
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(this.getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
接着是分析 this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties()方法,在上述我们已经提到 getEnvironment()返回的不再是默认的 StandardEnvironment 而是替换为了 StandardServletEnvironment,在此基础上查找 validateRequiredProperties()的实现方法,最终定位到了 AbstractEnvironment 类中:
public void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException {
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
}
this.propertyResolver 指的是 PropertySourcesPropertyResolver 对象,最终具体实现定位在 AbstractPropertyResolver 类中:
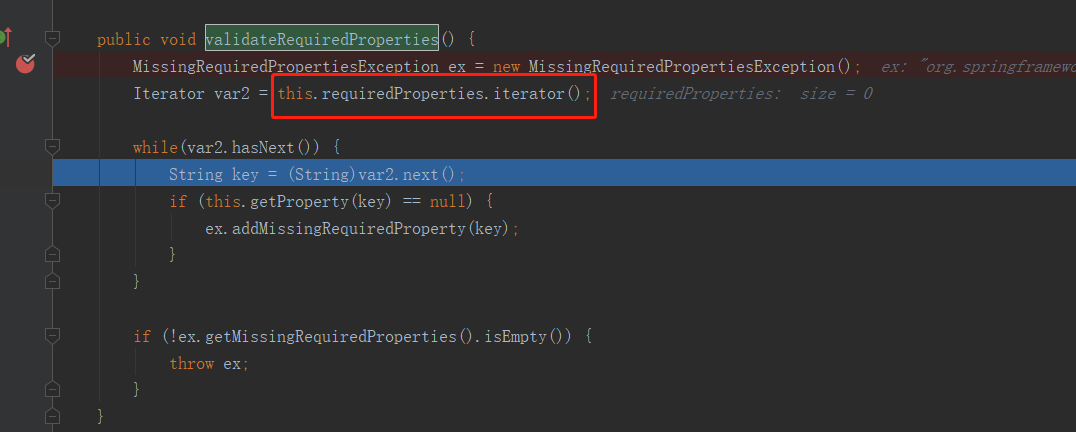
public void validateRequiredProperties() {
MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();
Iterator var2 = this.requiredProperties.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
String key = (String)var2.next();
if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {
ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {
throw ex;
}
}
3.2 obtainFreshBeanFactory
该方法的实现如下,通过 refreshBeanFactory 重置 AbstractApplicationContext 持有的 BeanFactory,然后通过 getBeanFactory 获取该对象并返回。
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
this.refreshBeanFactory();
return this.getBeanFactory();
}
AbstractApplicationContext 中 refreshBeanFacoty 方法和 getBeanFactory 方法都是抽象方法, 具体实现在 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 中。
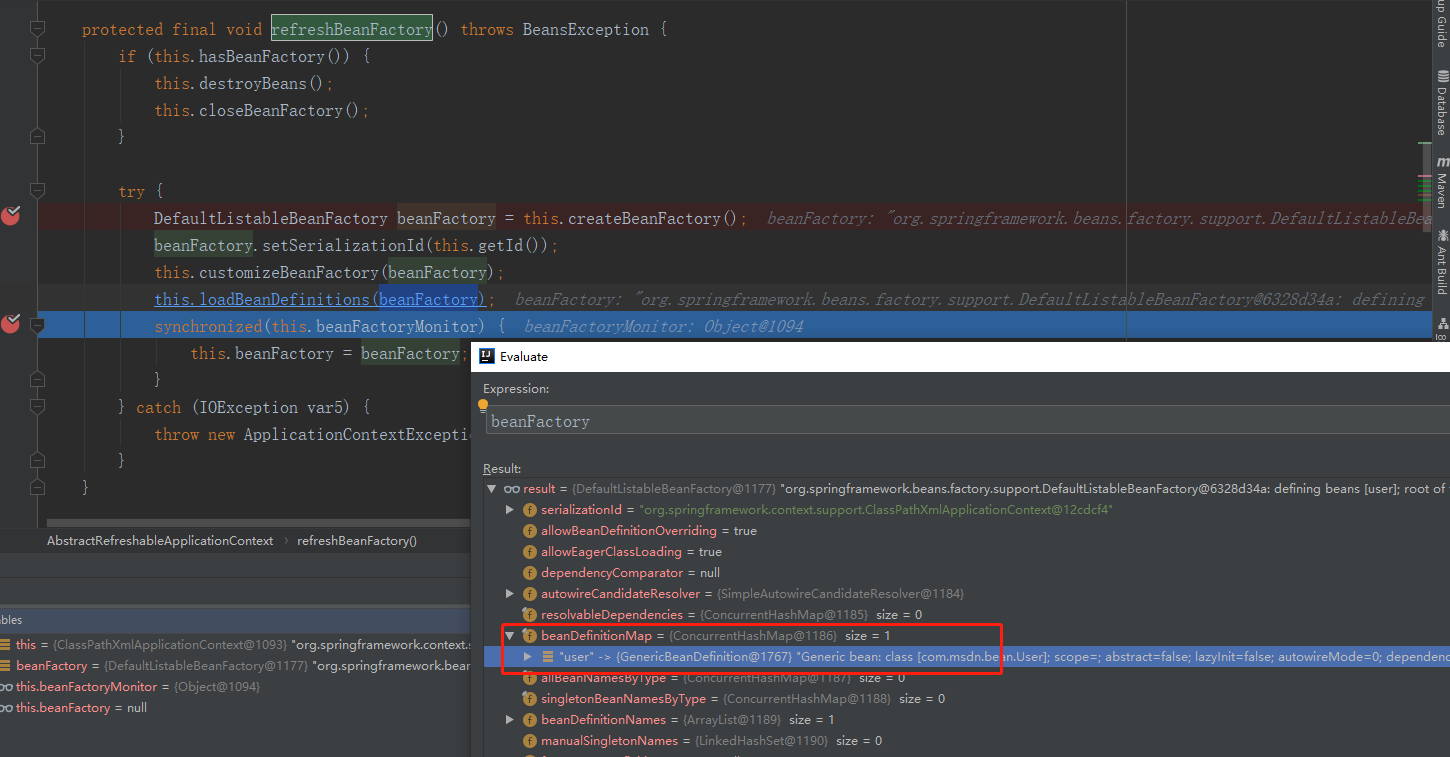
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (this.hasBeanFactory()) {
//销毁已经存在的单例bean
this.destroyBeans();
//销毁已有的BeanFactory
this.closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建一个新的beanFactory,类型为DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory();
//设置序列化id,为实例对象内存中的十六进制标识
beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
//定制beanFactory,设置相关属性,包括是否允许覆盖同名称的不同定义的对象以及循环依赖以及设置
this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//加载BeanDefiniton
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5);
}
}
loadBeanDefinitions 在 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 中是个抽象方法,具体实现是在 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 中:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//为当前工厂创建xml解析器
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//配置当前环境
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//配置资源解析器
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
//配置schemas或者dtd的资源解析器,EntityResolver维护了url->schemalocation的路径
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
//子类提供自定义的reader的初始化方法
this.initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//加载bean定义
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
在 loadBeanDefinitions 方法中传入了 DefaultListableBeanFactory 对象,并且初始化了 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 对象,接着就是初始化 bean 工厂的一些环境、类加载器等。 继续进入到 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader)方法体中,代码如下:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = this.getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = this.getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
这里的 configResources 和 configLocations 对应两种构造函数,其中 configLocations 是构造函数A使用的。关于 loadBeanDefinitions 方法涉及的内容比较多,我们挑一些重要的来看。以下是 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 类中的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = this.getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
} else {
int count;
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver)resourceLoader).getResources(location);
count = this.loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
} catch (IOException var6) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", var6);
}
} else {
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
count = this.loadBeanDefinitions((Resource)resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
}
上述方法主要做两件事:
- 调用资源加载器获取资源 resourceLoader.getResource(location) 。
- 真正执行加载功能的是子类 XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法 。
其中 getResources 方法是在 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 类实现的。
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) {
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length())) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : this.findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length()));
} else {
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : locationPattern.indexOf(58) + 1;
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : new Resource[]{this.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
count = this.loadBeanDefinitions(resources);中的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法具体实现在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类中。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = (Set)this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!((Set)currentResources).add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
} else {
int var5;
try {
//将资源文件转换为类型为InputStream的I/O流
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
//从InputStream中得到xML的解析源
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
//编码如果不为null, 则设置inputSource的编码
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
var5 = this.doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
} finally {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException var15) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), var15);
} finally {
((Set)currentResources).remove(encodedResource);
if (((Set)currentResources).isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
return var5;
}
}
getInputStream 方法用来加载 XML 文件,具体实现在 ClassPathResource 类中,
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
} else {
return is;
}
}
doLoadBeanDefinitions 用来注册 bean。
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//转化为Document 对象
Document doc = this.doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//启动对Bean定义解析的详细过程,会用到Spring Bean的配置规则
int count = this.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) {
throw var5;
.....
}
后续关联的代码在此就不做介绍,后期我们再学习。
因为在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 中已经将之前初始化的 DefaultListableBeanFactory 注册进去了,所以 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 所读取的 BeanDefinitionHolder 都会注册到 DefinitionListableBeanFactory 中,也就是经过这个步骤,DefaultListableBeanFactory 的变量 beanFactory 已经包含了所有解析好的配置。
至此通过加载 XML 文件, 将xml文件解析为对应的 BeanDefinition ,完成了 Bean 定义的加载和注册。
3.3 prepareBeanFactory
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//设置beanFactory的classLoader为当前context的classloader
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(this.getClassLoader());
//设置beanFactory的表达式语言处理器,Spring3增加了表达式语言的支持,
//默认可以使用#{bean.xxx}的形式来调用相关属性值
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//设置PropertyEditorRegistrar,通过PropertyEditor将xml解析出来的bean属性(字符串)和相应的java类型做转换
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, this.getEnvironment()));
/**
添加后置处理器ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,在Bean初始化后自动执行各Aware接口的set方法,包 括ResourceLoaderAware、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware、 ApplicationContextAware、EnvironmentAware
**/
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
//预先设置用于自动依赖注入的接口对象
//包括BeanFactory、ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、ApplicationContext
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
//在 bean 实例化后,添加ApplicationListenerDetector,可以理解成:注册事件监听器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
//如果存在loadTimeWeaver这个Bean,则增加对应的后置处理器
if (beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver")) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
//添加默认的系统环境bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean("environment")) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("environment", this.getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean("systemProperties")) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("systemProperties", this.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean("systemEnvironment")) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("systemEnvironment", this.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
其中反复出现了 addBeanPostProcessor 方法,该方法具体实现在 AbstractBeanFactory 类中。
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
}
详细分析下代码发现上面函数主要是在以下方法进行了扩展:
- 对SPEL语言的支持
- 增加对属性编辑器的支持
- 增加对一些内置类的支持,如EnvironmentAware、MessageSourceAware的注入
- 设置了依赖功能可忽略的接口
- 注册一些固定依赖的属性
- 如果存在loadTimeWeaver这个Bean,则增加对应的后置处理器
- 将相关环境变量及属性以单例模式注册
3.4 postProcessBeanFactory
所有 Bean 的定义已经加载完成,但是没有实例化,这一步可以修改 bean 定义或者增加自定义的 bean。该方法主要是承接上文中的 prepareBeanFactory 方法,增加一些后置处理器。具体实现在 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 类中。
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//增加ServletContextAwareProcessor后置处理器
//用于处理ServletContextAware接口和ServletConfigAware接口中相关对象的自动注入
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
//注册web环境,包括request、session、golableSession、application
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
//注册servletContext、contextParamters、contextAttributes、servletConfig单例bean
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
3.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, this.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver")) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
在执行 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法前查看 beanFactory,对比执行后发现此处有所不同。
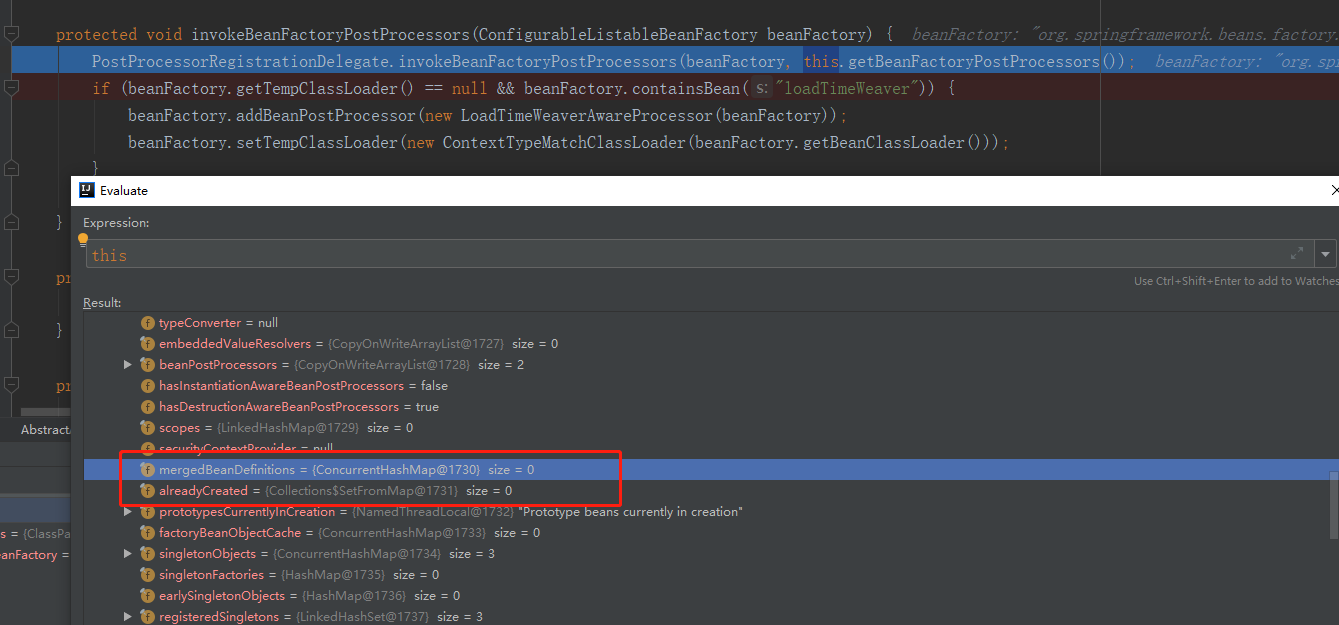
在 Spring 容器中找出实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 Bean 并执行。Spring 容器会委托给 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法执行。这里提到的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 如果不了解,可以参考这篇文章:Spring之BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
通过调试发现,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 类中的 beanFactoryPostProcessors 属性为空,所以执行 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法时也是如此。
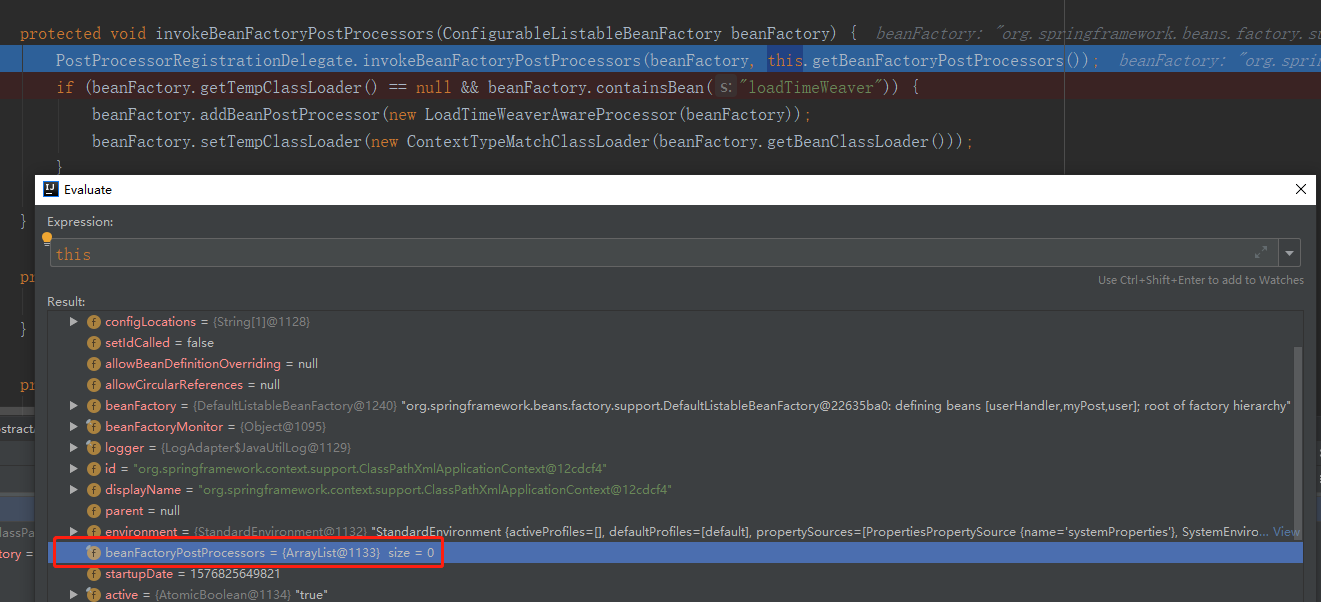
那么我们执行该方法有什么用呢?那么还有什么地方可能存在实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 Bean,带着疑问,我们去查看 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 中的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法。
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet();
ArrayList regularPostProcessors;
ArrayList registryProcessors;
int var9;
....
}
这一段代码特别长,一开始看起来肯定觉得很难,不知道从哪入手,这里我介绍一下我的学习方法,对测试代码进行 debug 调试,进入该方法后一步一步往下执行,遇到外部引用的方法记下来,待会调试完毕找到该方法,然后再打断点进行调试。反复来几遍,大概就能理解这个方法做了什么事情。
首先该方法的参数 beanFactory 实际类型为 DefaultListableBeanFactory,beanFactoryPostProcessors 参数内容为空。调试过程中发现比较重要的方法是 getBeanNamesForType 方法,该方法有三个参数值,具体实现在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 类中。
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
if (this.isConfigurationFrozen() && type != null && allowEagerInit) {
Map<Class<?>, String[]> cache = includeNonSingletons ? this.allBeanNamesByType : this.singletonBeanNamesByType;
String[] resolvedBeanNames = (String[])cache.get(type);
if (resolvedBeanNames != null) {
return resolvedBeanNames;
} else {
resolvedBeanNames = this.doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, true);
if (ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(type, this.getBeanClassLoader())) {
cache.put(type, resolvedBeanNames);
}
return resolvedBeanNames;
}
} else {
return this.doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
}
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法代码在调用 getBeanNamesForType 方法时根据第一个参数类型的不同分为两类: BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 。其中 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 继承自 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。执行的时候,先找出所有的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 执行再找出所有 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 执行。因为 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 继承自 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,所以执行后者时会过滤掉前者的内容。
在调试中发现只有当参数为 BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class 时,才会获取到有效的内容。 getBeanNamesForType 方法中的关键部分是 doGetBeanNamesForType 方法,该方法主要是将 XML 文件中定义的实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的 bean 的 id 取出来,以及将 XML 文件中定义的 bean 加载到 beanFactory 中。
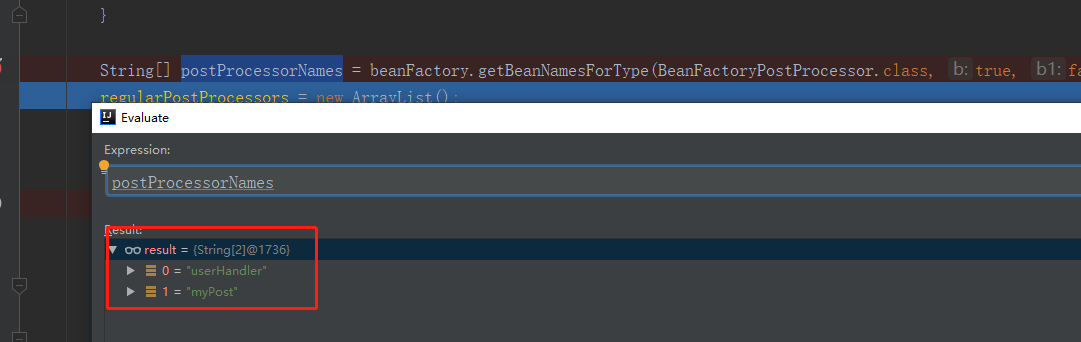
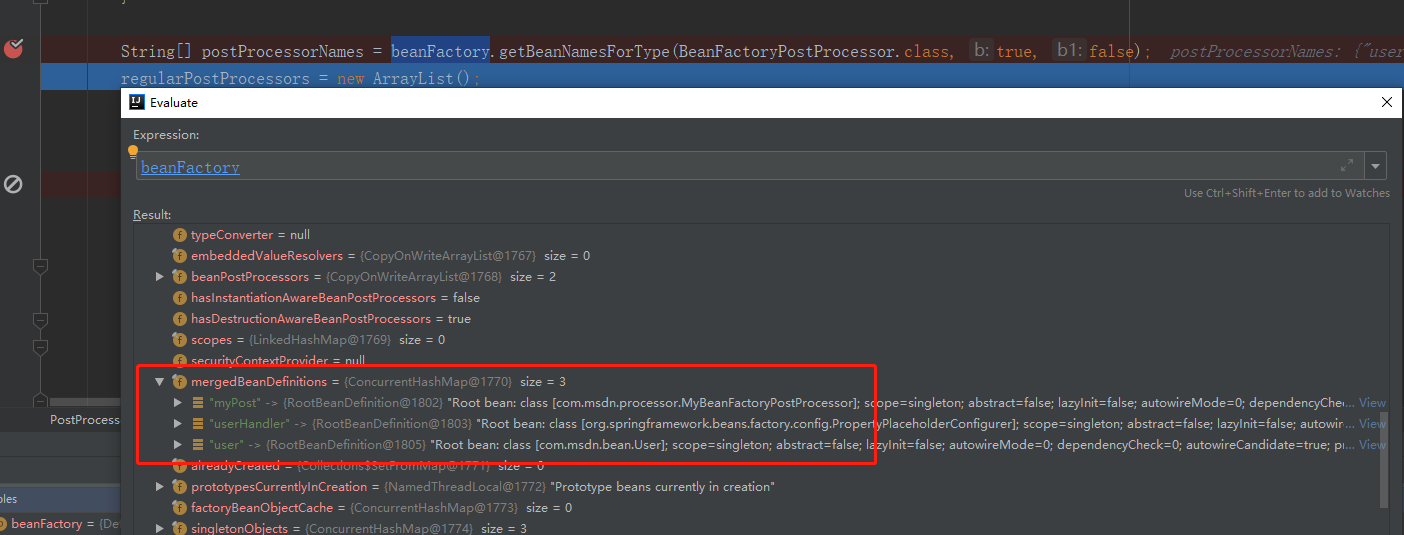
等待 getBeanNamesForType 返回这些内容后,接着就会实例化并初始化实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的类并执行。这里比较关键的代码是 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 和 PropertyResourceConfigurer 类中的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Iterator var2 = postProcessors.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor)var2.next();
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
Properties mergedProps = this.mergeProperties();
this.convertProperties(mergedProps);
this.processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
} catch (IOException var3) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", var3);
}
}
当 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法执行完毕后,查看 beanFactory 的状态。
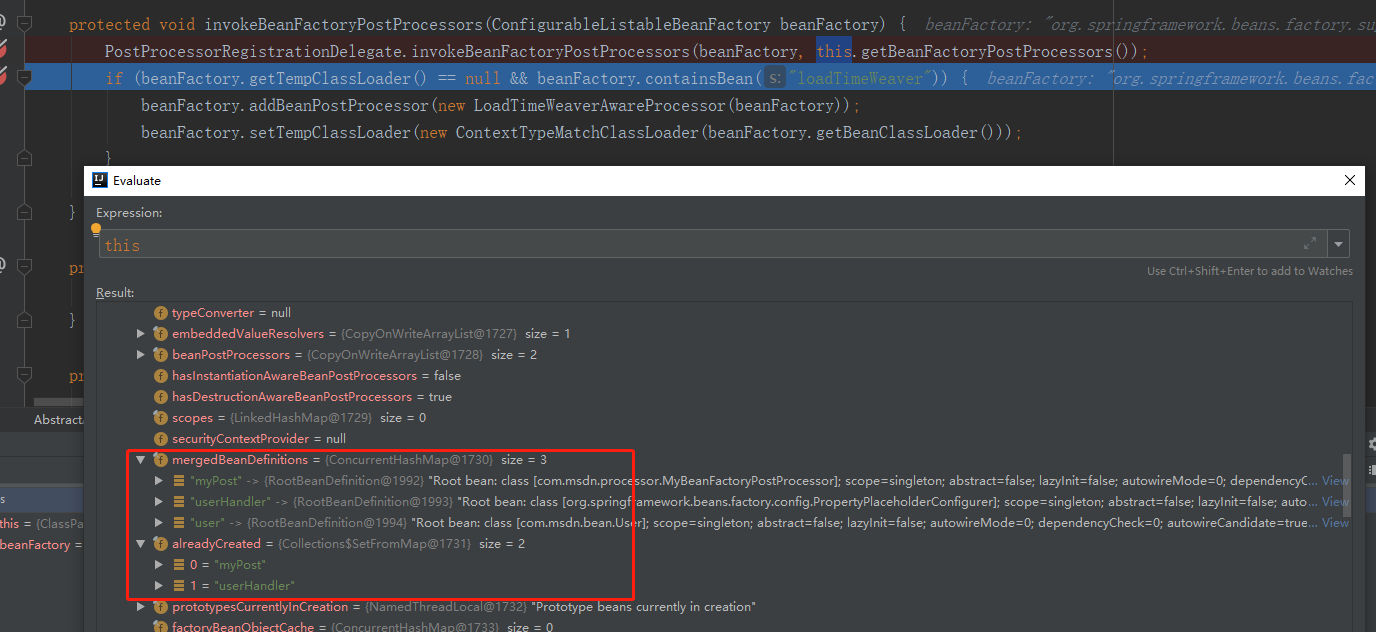
3.6 registerBeanPostProcessors
从 Spring 容器中找出的 BeanPostProcessor 接口的 Bean,并添加到 BeanFactory 内部维护的 List 属性中,以便后续 Bean 被实例化的时候调用这个 BeanPostProcessor进行回调处理。该方法委托给了 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 类的 registerBeanPostProcessors 方法执行。
同 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 类似, 先从容器中获取所有类型为 BeanPostProcessor.class 的 Bean 的 name 数组,然后通过 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 获取Bean的实例,最后通过 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);将获取到的 BeanPostProcessor 实例添加到容器的属性中。在实际过程中会根据 AbstractBeanFactory 类中的 isTypeMatch 方法对 bean 实例进行筛选,具体顺序为:
- 将实现 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanPostProcessor 列表添加到 beanFactory 中
- 将实现 Ordered 接口的 BeanPostProcessor 列表添加到 beanFactory 中
- 将剩余的 BeanPostProcessor 列表添加到 beanFactory 中
- 将实现 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 接口的 BeanPostProcessor 列表添加到 beanFactory 中
另外在 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 类中有个内部类 BeanPostProcessorChecker,它实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,所以最后会有一个 BeanPostProcessorChecker 类添加到 beanFactory 中。
最终该方法用来实例化并初始化实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口的类,但不执行。
3.7 initMessageSource
在 Spring 容器中初始化一些国际化相关的属性 。
3.8 initApplicationEventMulticaster
初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaste (事件广播器)是在方法 initApplicationEventMulticaster()中实现的,进入到方法体,如下:
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory();
// 1、默认使用内置的事件广播器,如果有的话.
// 我们可以在配置文件中配置Spring事件广播器或者自定义事件广播器
// 例如: <bean id="applicationEventMulticaster" class="org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster"></bean>
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean("applicationEventMulticaster")) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = (ApplicationEventMulticaster)beanFactory.getBean("applicationEventMulticaster", ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
} else {
// 2、否则,新建一个事件广播器,SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster是spring的默认事件广播器
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton("applicationEventMulticaster", this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("No 'applicationEventMulticaster' bean, using [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
通过源码可以看出该方法实现逻辑与 initMessageSource 基本相同,其步骤如下:查找是否有 name 为 applicationEventMulticaster 的 bean,如果有则放到容器里,如果没有,初始化一个系统默认的 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 对象放入容器。
3.9 onRefresh
模块方法,可用于 refresh 动作的扩展,默认为空实现。在 SpringBoot 中主要用于启动内嵌的 Web 服务器。
3.10 registerListeners
注册监听器,找出系统中的 ApplicationListener 对象,注册到时间广播器中。如果有需要提前进行广播的事件,则执行广播。
protected void registerListeners() {
// 首先,注册指定的静态事件监听器,在spring boot中有应用
Iterator var1 = this.getApplicationListeners().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener = (ApplicationListener)var1.next();
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// 其次,注册普通的事件监听器
String[] listenerBeanNames = this.getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
String[] var7 = listenerBeanNames;
int var3 = listenerBeanNames.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
String listenerBeanName = var7[var4];
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// 如果有早期事件的话,在这里进行事件广播
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
Iterator var9 = earlyEventsToProcess.iterator();
while(var9.hasNext()) {
ApplicationEvent earlyEvent = (ApplicationEvent)var9.next();
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
3.11 finishBeanFactoryInitialization
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 判断有无ConversionService(bean属性类型转换服务接口),并初始化
if (beanFactory.containsBean("conversionService") && beanFactory.isTypeMatch("conversionService", ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService((ConversionService)beanFactory.getBean("conversionService", ConversionService.class));
}
// 如果beanFactory中不包含EmbeddedValueResolver,则向其中添加一个EmbeddedValueResolver
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {// EmbeddedValueResolver-->解析bean中的占位符和表达式
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver((strVal) -> {
return this.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
});
}
// 初始化LoadTimeWeaverAware类型的bean
// LoadTimeWeaverAware-->加载Spring Bean时织入第三方模块,如AspectJ
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
String[] var3 = weaverAwareNames;
int var4 = weaverAwareNames.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String weaverAwareName = var3[var5];
this.getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// 释放临时类加载器
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader((ClassLoader)null);
// 冻结缓存的BeanDefinition元数据
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 初始化其他的非延迟加载的单例bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
实例化 BeanFactory 中已经被注册但是未实例化的所有实例(懒加载的不需要实例化),主要操作是 BeanFactory 的 preInstantiateSingletons 方法。该方法分为两部分:
- 遍历已经解析出来的所有 beanDefinitionNames,如果该 BeanDefinition 不是抽象类、是单例且没有设置懒加载,则进行实例化和初始化。
- 遍历解析出来的 beanDefinitionNames,如果获得的单例是 SmartInitializingSingleton 的实现类,则会执行 afterSingletonsInstantiated 方法。注意该方法调用只会发生在启动阶段,后续懒加载对象再初始化的时候,不会再进行回调。
3.12 finishRefresh
完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器 lifecycleProcessor 刷新过程,同时发出 ContextRefreshEvent 通知。
protected void finishRefresh() {
// 清空资源缓存
this.clearResourceCaches();
// 初始化生命周期处理器
this.initLifecycleProcessor();
// 调用生命周期处理器的onRefresh方法
this.getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// 推送容器刷新事件
this.publishEvent((ApplicationEvent)(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)));
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}